今天在fedora13下破解wep,懒得总是复制MAC了,想能不能在fedora上也安装上SpoonWep2呢,找了半天也没有rpm的包.后来发现直接把deb的包解出来,把文件直接复制到系统对应目录就可以运行了,很简单嘛:) .后来又发现问题了.在shell中运行,找不到网出现这个错误 /usr/local/bin/wifispoonfeeder/spoonwep/tmp/wscapture-01.txt 在网上找找了,发现在出现这个错误时,再打开一个shell运行ln -s /usr/local/bin/wifispoonfeeder/spoonwep/tmp/wscapture-01.csv /usr/local/bin/wifispoonfeeder/spoonwep/tmp/wscapture-01.txt 命令就可以解决了,但是每次搜网都要运行一次.
IP 分片与重组
IP:分片与重组
1. 引言
为了与互联网上的任意计算机通信,每个应用TCP/IP的计算机必须具有分片和重组的代码,一个设计良好的应用软件,会生成足够小的数据报,
因此主机并不需要经常执行分片任务.
2. 数据报的分片
分片发生在选择路由之后,以及放入接口队列之前.IP把数据报长度与MTU进行比较,确定是否需要分片.
如需分片,IP首先生成多个数据报,并将每个数据报中的分片位置1,将源数据报中的数据按顺序分片,并将它们装入这些数据报中.
它还在同一源数据报产生的所有数据报片中将MF位置为1,末尾片除外.IP一边分片,一边将它们传递给网络接口发送出去.
2.1 为一个数据报片再次分片
对于MF未置1的片,和上边说的没区别,除了最后一个片外,其它全置1.但对于MF为1的源片,再次分片后的所有分片MF全置1
3. 分片的实现
/* ipputp.c – ipputp */
#include <conf.h>
#include <kernel.h>
#include <network.h>
/*————————————————————————
* ipputp – 发送一个数据包到一个接口的输出队列
*————————————————————————
*/
int
ipputp(unsigned ifn, IPaddr nh, struct ep *pep)
{
struct netif *pni = &nif[ifn]; /* 接口指针*/
struct ip *pip; /* IP报指针*/
int hlen, maxdlen, tosend, offset, offindg;
if (pni->ni_state == NIS_DOWN) { /* 接口关闭则返回*/
freebuf(pep);
return SYSERR;
}
pip = (struct ip *)pep->ep_data; /* IP报指向*/
if (pip->ip_len <= pni->ni_mtu) { /* IP报长度小于等于接口MTU,则直接发送数据报*/
pep->ep_nexthop = nh;
pip->ip_cksum = 0;
iph2net(pip);
pep->ep_order &= ~EPO_IP;
pip->ip_cksum = cksum((WORD *)pip, IP_HLEN(pip));
return netwrite(pni, pep, EP_HLEN+net2hs(pip->ip_len));
}
/* 否则,我们必须分片 */
if (pip->ip_fragoff & IP_DF) { /* 能否分片,不能分片则报错并返回*/
IpFragFails++;
icmp(ICT_DESTUR, ICC_FNADF, pip->ip_src, pep, 0);
return OK;
}
maxdlen = (pni->ni_mtu – IP_HLEN(pip)) &~ 7; /* 最大长度为MTU减去IP头长度,并增加到8的倍数*/
offset = 0; /* 偏移量*/
offindg = (pip->ip_fragoff & IP_FRAGOFF)<<3; /* 偏移量,保存控制位*/
tosend = pip->ip_len – IP_HLEN(pip); /* 要发送的IP报长度,不包括IP报头*/
while (tosend > maxdlen) { /* 仅当剩余的数据大于可发送的最大数据量时才发送*/
if (ipfsend(pni,nh,pep,offset,maxdlen,offindg) != OK) { /* 生成并发送分片*/
IpOutDiscards++;
freebuf(pep);
return SYSERR;
}
IpFragCreates++;
tosend -= maxdlen;
offset += maxdlen;
offindg += maxdlen; /* */
}
IpFragOKs++;
IpFragCreates++;
hlen = ipfhcopy(pep, pep, offindg); /* 首部拷贝处理,返回首部长度*/
pip = (struct ip *)pep->ep_data; /* 取IP数据报*/
/*处理最后一个分片,当最后剩余的数据小于等于可发送的最大数据量 */
memcpy(&pep->ep_data[hlen], &pep->ep_data[IP_HLEN(pip)+offset],
tosend); /* 修改源报,使之变为最后一个报片*/
/*非末尾的数据报片再次分片时,保证MF全为1 */
pip->ip_fragoff = (pip->ip_fragoff & IP_MF)|(offindg>>3);
pip->ip_len = tosend + hlen;
pip->ip_cksum = 0;
iph2net(pip);
pep->ep_order &= ~EPO_IP;
pip->ip_cksum = cksum((WORD *)pip, hlen);
pep->ep_nexthop = nh;
return netwrite(pni, pep, EP_HLEN+net2hs(pip->ip_len));
}
3.1 发送一个数据报片
/* ipfsend.c – ipfsend */
#include <conf.h>
#include <kernel.h>
#include <network.h>
int ipfhcopy(struct ep *, struct ep *, unsigned);
/*————————————————————————
* ipfsend – 发送一个IP数据报的分片
*————————————————————————
*/
int
ipfsend(struct netif *pni, IPaddr nexthop, struct ep *pep,
unsigned offset, unsigned maxdlen, unsigned offindg)
{
struct ep *pepnew;
struct ip *pip, *pipnew;
int hlen, len;
pepnew = (struct ep *)getbuf(Net.netpool); /* 申请一个新帧的缓冲区*/
if (pepnew == (struct ep *)SYSERR)
return SYSERR;
pepnew->ep_order = ~0;
hlen = ipfhcopy(pepnew, pep, offindg); /* 复制头 */
pip = (struct ip *)pep->ep_data; /* 源IP报的指向*/
pipnew = (struct ip *)pepnew->ep_data; /* 新生成的IP报*/
pipnew->ip_fragoff = IP_MF | (offindg>>3);
pipnew->ip_len = len = maxdlen + hlen;
pipnew->ip_cksum = 0;
iph2net(pipnew);
pepnew->ep_order &= ~EPO_IP; /* 清除字节顺序*/
pipnew->ip_cksum = cksum((WORD *)pipnew, hlen);
memcpy(&pepnew->ep_data[hlen], /* 复制数据*/
&pep->ep_data[IP_HLEN(pip)+offset], maxdlen);
pepnew->ep_nexthop = nexthop;
return netwrite(pni, pepnew, EP_HLEN+len); /* 发送并返回 */
}
3.2 复制数据报首部
/* ipfhcopy.c – ipfhcopy */
#include <conf.h>
#include <kernel.h>
#include <network.h>
/*————————————————————————
* ipfhcopy – copy the hardware, IP header, and options for a fragment
*————————————————————————
*/
int
ipfhcopy(struct ep *pepto, struct ep *pepfrom, unsigned offindg)
{
struct ip *pipfrom = (struct ip *)pepfrom->ep_data; /* 旧IP报*/
unsigned i, maxhlen, olen, otype;
unsigned hlen = (IP_MINHLEN<<2); /* IP头最小长度*4 ,就是以字节为单位了*/
if (offindg == 0) { /* 偏移为0,说明是第一个分片,复制帧的头和IP头到新的帧*/
memcpy(pepto, pepfrom, EP_HLEN+IP_HLEN(pipfrom));
return IP_HLEN(pipfrom);
}
/* 以下就说明不是第一个IP分片了*/
memcpy(pepto, pepfrom, EP_HLEN+hlen); /* 复制帧的头和除了IP选项外的报头*/
/*复制选项 */
maxhlen = IP_HLEN(pipfrom); /* 包括选项的IP头的长度*/
i = hlen; /* 不包括选项的IP头长度*/
while (i < maxhlen) { /* 最小头比最大头小,说明有IP选项*/
otype = pepfrom->ep_data[i]; /* IP选项*/
olen = pepfrom->ep_data[++i]; /* 选项长度*/
if (otype & IPO_COPY) { /* 如果复制位为1*/
memcpy(&pepto->ep_data[hlen],
&pepfrom->ep_data[i-1], olen); /* 复制这个选项到所有新的帧*/
hlen += olen;
} else if (otype == IPO_NOP || otype == IPO_EOOP) { /* 选项结束或没有操作*/
pepto->ep_data[hlen++] = otype;
olen = 1;
}
i += olen-1;
if (otype == IPO_EOOP)
break;
}
/* pad to a multiple of 4 octets */
while (hlen % 4) /* 填充到4字节的整数倍*/
pepto->ep_data[hlen++] = IPO_NOP;
return hlen;
}
4. 数据报的重组
4.1 数据结构
/* ipreass.h */
/* Internet Protocol (IP) reassembly support */
#define IP_FQSIZE 10 /* 分片队列的数大数量 */
#define IP_MAXNF 10 /* 分片/数据报 的最大数量 */
#define IP_FTTL 60 /* 生存时间(秒)*/
/* ipf_state flags */
#define IPFF_VALID 1 /* 内容是有效的 */
#define IPFF_BOGUS 2 /* 丢弃 */
#define IPFF_FREE 3 /* 这个队列可以自由分配 */
struct ipfq {
char ipf_state; /* 队列状态,值为上边 3种 */
IPaddr ipf_src; /* 源IP地址 */
short ipf_id; /* 数据报ID */
int ipf_ttl; /* 数据报重组的生存时间 */
int ipf_q; /* 分片存储的链表 */
};
extern int ipfmutex; /* 互斥 mutex for ipfqt[] */
extern struct ipfq ipfqt[]; /* IP分片队列表 */
int ipfsend(struct netif *, IPaddr, struct ep *, unsigned, unsigned,
unsigned);
int ipfhcopy(struct ep *, struct ep *, unsigned);
4.2 互斥操作
为了何证进程在数据报片的链表时不会互相干扰,重组程序代码使用了一个互斥信号量ipfmutex.在ipreass.h中
4.3 在链表中加入一个数据报片
/* ipreass.c – ipreass */
#include <conf.h>
#include <kernel.h>
#include <network.h>
int ipfadd(struct ipfq *, struct ep *);
struct ep *ipfjoin(struct ipfq *);
/*————————————————————————
* ipreass – reassemble an IP datagram, if necessary
* returns packet, if complete; 0 otherwise
* IP数据报重组,如果报片到齐则重组该包,并返回完整的数据报,否则返回0
*————————————————————————
*/
struct ep *
ipreass(struct ep *pep)
{
struct ep *pep2;
struct ip *pip;
int firstfree;
int i;
pip = (struct ip *)pep->ep_data; /* 得到IP数据报的*/
wait(ipfmutex); /* 互斥*/
if ((pip->ip_fragoff & (IP_FRAGOFF|IP_MF)) == 0) { /*如果不是分片,返回当前帧*/
signal(ipfmutex);
return pep;
}
IpReasmReqds++;
firstfree = -1;
/* 以下情况为是分片 */
for (i=0; i<IP_FQSIZE; ++i) {
struct ipfq *piq = &ipfqt[i];
if (piq->ipf_state == IPFF_FREE) { /* 队列未使用,则继续*/
if (firstfree == -1)
firstfree = i;
continue;
}
if (piq->ipf_id != pip->ip_id) /* 队列ID不等于分片ID,则继续*/
continue;
if (piq->ipf_src != pip->ip_src) /* 源地址不同,则继续*/
continue;
/* 找到匹配 */
if (ipfadd(piq, pep) == 0) { /* 把该分片加入匹配的队列*/
signal(ipfmutex);
return 0;
}
pep2 = ipfjoin(piq); /* 检查是否可以重组数据报*/
signal(ipfmutex);
return pep2;
}
/* 没有匹配 */
if (firstfree < 0) { /* 检查是否有空闲队列*/
/* no room– drop */ /* 没有空闲则丢弃*/
freebuf(pep);
signal(ipfmutex);
return 0;
}
ipfqt[firstfree].ipf_q = newq(IP_FQSIZE, QF_WAIT); /* 分配一个空闲表项*/
if (ipfqt[firstfree].ipf_q < 0) {
freebuf(pep);
signal(ipfmutex);
return 0;
}
ipfqt[firstfree].ipf_src = pip->ip_src; /* 填充*/
ipfqt[firstfree].ipf_id = pip->ip_id;
ipfqt[firstfree].ipf_ttl = IP_FTTL;
ipfqt[firstfree].ipf_state = IPFF_VALID;
ipfadd(&ipfqt[firstfree], pep);
signal(ipfmutex);
return 0;
}
int ipfmutex;
struct ipfq ipfqt[IP_FQSIZE];
4.4 溢出时的丢弃
/* ipfadd.c – ipfadd */
#include <conf.h>
#include <kernel.h>
#include <proc.h>
#include <network.h>
/*————————————————————————
* ipfadd – 增加一个分片到一个IP碎片队列
*————————————————————————
*/
Bool
ipfadd(struct ipfq *iq, struct ep *pep)
{
struct ip *pip;
int fragoff;
if (iq->ipf_state != IPFF_VALID) { /* 分片队列无效,则丢弃*/
freebuf(pep);
return FALSE;
}
pip = (struct ip *)pep->ep_data; /* 得到IP数据报的*/
fragoff = pip->ip_fragoff & IP_FRAGOFF; /* 得到偏移量*/
/* -fragoff用作关键值,越大越靠前 */
if (enq(iq->ipf_q, pep, -fragoff) < 0) { /* 举出丢弃并释放内存*/
/* overflow– free all frags and drop */
freebuf(pep);
IpReasmFails++;
while (pep = (struct ep *)deq(iq->ipf_q)) { /* 从队列删除帧并释放帧*/
freebuf(pep);
IpReasmFails++;
}
freeq(iq->ipf_q); /* 释放队列*/
iq->ipf_state = IPFF_BOGUS;
return FALSE;
}
iq->ipf_ttl = IP_FTTL; /* 重置生存时间 */
return TRUE;
}
4.5 测试一个完整的数据据报
/* ipfjoin.c – ipfjoin */
#include <conf.h>
#include <kernel.h>
#include <proc.h>
#include <network.h>
struct ep *ipfcons(struct ipfq *);
/*————————————————————————
* ipfjoin – join fragments, if all collected
*————————————————————————
*/
struct ep *
ipfjoin(struct ipfq *iq)
{
struct ep *pep;
struct ip *pip = 0;
int off, packoff;
if (iq->ipf_state == IPFF_BOGUS)
return 0;
/* see if we have the whole datagram */
/* 看我们是否有整个的数据包 */
off = 0;
while (pep=(struct ep *)seeq(iq->ipf_q)) { /* 取出帧*/
pip = (struct ip *)pep->ep_data; /* 取出IP报*/
packoff = (pip->ip_fragoff & IP_FRAGOFF)<<3;
if (off < packoff) { /* 偏移大于0*/
while(seeq(iq->ipf_q)) /* 一个不满足,说没没全到*/
/*empty*/;
return 0;
}
off = packoff + pip->ip_len – IP_HLEN(pip); /*计算总长度,不含头*/
}
/* 这里利用off来测试,首先ipfjoin查看当前数据报片的偏移量是否与off值相符。
如果当前数据报片的偏移量超过了off的值,那么必定有尚未到达的数据报片,
因此ipfjoin返回0。如果偏移量与off值一致,那么ipfjoin通过将off值加上当前
数据报片长度减去首部计算出下一个数据报片的偏移量。*/
if (off > MAXLRGBUF) { /* 超过缓冲区则丢弃 – too big for us to handle */
while (pep = (struct ep *)deq(iq->ipf_q))
freebuf(pep);
freeq(iq->ipf_q);
iq->ipf_state = IPFF_FREE;
return 0;
}
if (pip == 0 || (pip->ip_fragoff & IP_MF) == 0) /* 没有IP报或没有更多的分片*/
return ipfcons(iq); /* 收集数据报片并重建完整的数据报 */
return 0;
}
4.6 将数据报片组装成完整的数据报
/* ipfcons.c – ipfcons */
#include <conf.h>
#include <kernel.h>
#include <network.h>
/*————————————————————————
* ipfcons – 从IP碎片队列构建一个分组
*————————————————————————
*/
struct ep *
ipfcons(struct ipfq *iq)
{
struct ep *pep, *peptmp;
struct ip *pip;
int off, seq;
pep = (struct ep *)getbuf(Net.lrgpool); /* 申请缓存空间*/
if (pep == (struct ep *)SYSERR) { /* 申请失败则丢弃该报*/
while (peptmp = (struct ep *)deq(iq->ipf_q)) {
IpReasmFails++;
freebuf(peptmp);
}
freeq(iq->ipf_q); /* 释放队列*/
iq->ipf_state = IPFF_FREE;
return 0;
}
/* 复制帧和IP报头 */
peptmp = (struct ep *)deq(iq->ipf_q); /* 取出一个分片*/
pip = (struct ip *)peptmp->ep_data; /* 得到IP报*/
off = IP_HLEN(pip); /* 得到IP头长度*/
seq = 0;
memcpy(pep, peptmp, EP_HLEN+off); /* 复制IP报头到pep*/
/* 复制数据部分 */
while (peptmp != 0) {
int dlen, doff;
pip = (struct ip *)peptmp->ep_data; /* 取IP报*/
doff = IP_HLEN(pip) + seq
– ((pip->ip_fragoff&IP_FRAGOFF)<<3);
dlen = pip->ip_len – doff;
memcpy(pep->ep_data+off, peptmp->ep_data+doff, dlen);
off += dlen;
seq += dlen;
freebuf(peptmp);
peptmp = (struct ep *)deq(iq->ipf_q);
}
/* 修复分组的头 */
pip = (struct ip *)pep->ep_data; /* 取出IP报*/
pip->ip_len = off; /* 修复长度*/
pip->ip_fragoff = 0; /* 修复偏移量*/
/* 释放资源 */
freeq(iq->ipf_q);
iq->ipf_state = IPFF_FREE;
IpReasmOKs++;
return pep;
}
5. 数据报片链表的维护管理
/* ipftimer.c – ipftimer */
#include <conf.h>
#include <kernel.h>
#include <network.h>
/*————————————————————————
* ipftimer – 更新生存周期并删除过期的碎片
*————————————————————————
*/
void
ipftimer(int gran)
{
struct ep *pep;
struct ip *pip;
int i;
wait(ipfmutex); /* 申请互斥量 */
for (i=0; i<IP_FQSIZE; ++i) { /* 遍历队列*/
struct ipfq *iq = &ipfqt[i];
if (iq->ipf_state == IPFF_FREE) /* 空闲则继续*/
continue;
iq->ipf_ttl -= gran; /* 非空闲则ttl-1*/
if (iq->ipf_ttl <= 0) { /* 生存周期到达则*/
if (iq->ipf_state == IPFF_BOGUS) { /* 如果为丢弃状态,则继续*/
/* resources already gone */
iq->ipf_state = IPFF_FREE;
continue;
}
if (pep = (struct ep *)deq(iq->ipf_q)) { /* 取分片*/
IpReasmFails++;
pip = (struct ip *)pep->ep_data; /* 取IP报*/
icmp(ICT_TIMEX, ICC_FTIMEX, /* 向源站报错*/
pip->ip_src, pep, 0);
}
while (pep = (struct ep *)deq(iq->ipf_q)) { /* 释放资源*/
IpReasmFails++;
freebuf(pep);
}
freeq(iq->ipf_q); /* 释放队列*/
iq->ipf_state = IPFF_FREE;
}
}
signal(ipfmutex); /* 互斥解锁*/
}
6. 初始化
/* ipfinit.c – ipfinit */
#include <conf.h>
#include <kernel.h>
#include <network.h>
/*————————————————————————
* ipfinit – initialize IP fragment queue data structures
*————————————————————————
*/
void
ipfinit(void)
{
int i;
ipfmutex = screate(1); /* 不多说了,简单,太~~~,这个看不明白就不用看了. 🙂 */
for (i=0; i<IP_FQSIZE; ++i)
ipfqt[i].ipf_state = IPFF_FREE;
}
联通 新情1+ ADSL一体机 破解 PPPOE 自动拨号 HG527c 522
今天去朋友家,他家刚升级的2M ADSL 给了一个新猫,说是猫,不如说是一个无线路由加猫的一体机,上边有四个lan口,但是只能用前两个,按机子后边写的密码进去,找了好几圈也没找到写PPPOE用户名和密码的地方.后来在网上查了查发现,又是联通这个垃圾定制的问题,把这个功能给去了,但是有个超级用户可以设置.密码在网上找的,
地址:http://192.168.1.1/cnc.html
用户名:bjcnchgw
密码:8mCnC@bj
这是北京联通的默认密码.可是网上人家都说,只要连上电话线,联通就会改掉这个密码,这时就只能通用TTL线来看密码了.啊~~~~~~~~~~我以经连上网了呀,我报着试试的心情试用了上边的账号,进去了,哈哈,很激动呀,上去二话不说,先把连接的rx069删了,这是联通用于选程控制的连接,然后停用了远程控制,千万别忘了保存.现在安全了.
回到连接那里,最上边有个******0_35的连接,把模式改成route就是路由,选中pppoe,然后写上AD的用户名和密码,保存,等猫从启再看看,是不是不用拨号就能上网了呢,哈哈
最后还是说一下,不要和我一样先连上电话线,先要关了远程控制再连,不是每个人都有我这么好的运气哎.
个人认为可能是连接的人太多,改密码的连接不是那么简易就能拨上去的,所以让我冲了空子
最后忘了说了,第3.4个lan可以在改0-35那个连接时选中,lan3,lan4还启用.他关了后两个lan口,我想是因adsl只能双拨号,而不能更多的人拨号,所以他给你的设备默认没给你自动拨号的功能,当然只能每台电脑来拨号了,所以只能两台电脑拨何必让你插更多的电脑呢,顺便说一下,用无线网卡连接上也可以拨号,再者说,ADSL本来也不主张多人共用,外地不是封了路由吗.就说明了这个,所以他用封端口和自动拨号的功能,来禁止两台以上的电脑共用一条ADSL.!!~~~~无耻呀!!!~~~~~~~~~~
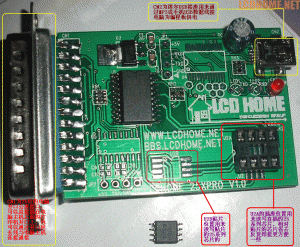
TP WR340G+ 541G+ 硬改 刷DD WRT 成功 固件 下载
改装后见下图
改装步骤:
1.准备8M flash MX25L6405D 8M SPI Flash 和 16位32M内存 与 编程器 LCDHOME论坛网并口25X系列编程板 淘宝上有卖10块
2.刷新8M flash 使用MX25L6405D与编程器
接线:(由于flash是16脚的,焊盘是8脚的,所以要转换)
1 7
2 8
3 9
4 10
5 15
6 16
7 1
8 2
IP 选路表 和 选路算法
1 引言
讨论选择路由的细节,选路表的结构,以及实现算法,路由如何使用子网掩码,如何区分网络路由子网路由以及主机路由
2 路由维护和查找
应当选择能使查找路由花费最小的IP数据结构和算法,维护路由的花费则并不那么重要
利用桶散列(bucket hashing)迅速找到正确的散列表元
3 选路表结构
保存路由的主要数据结构是数组。数组的每个元素对应一个散列表元,并包含一个指针,指向被装入这个散列表元中的通主目的站的路由记录链表。表中每个记录包含一个IP目的地址,子网掩码,下一跳地址,用于向下一跳地址发送数据的网络接口,以及其他的路由管理中使用的信息。由于IP预先并不知道子网掩码,它公使用IP目的地址的网络部分计算散列函数,在一个链表中查找表项时,使用的是完整的目的地址来进行比较。
4 选路表数据结构
/* route.h – RTFREE */
/* 路由表项 */
struct route {
IPaddr rt_net; /* 路由的目的地址 */
IPaddr rt_mask; /* 路由的掩码 */
IPaddr rt_gw; /* 下一跳的IP */
u_short rt_metric; /* 距离度量 */
u_short rt_ifnum; /* 接口的序号 */
short rt_key; /* 排序关键字 */
short rt_ttl; /* 生存时间(秒) */
struct route *rt_next; /* 哈希值指向下一个条目 */
/* stats */
int rt_refcnt; /* 引用计数 */
int rt_usecnt; /* 记录该路由使用的次数 */
};
/* 路由表的全局数据 */
struct rtinfo {
struct route *ri_default; /* 包含默认路由的下一跳地址 */
int ri_bpool; /* 结点的地址??? Route.ri_bpool = mkpool(sizeof(struct route), RT_BPSIZE) 现在还不太明白 */
Bool ri_valid; /* 此路由的数据结构是否被初始化 */
int ri_mutex; /* 互斥信号 */
};
#define RT_DEFAULT ip_anyaddr /* 默认的网络地址 全0 */
#define RT_LOOPBACK ip_loopback /* 回环地址 */
#define RT_TSIZE 512 /* 散列表长度??-these are pointers; it’s cheap */
#define RT_INF 999 /* 路由永不超时 */
#define RTM_INF 16 /* 一个最大距离度量 – an infinite metric */
/* rtget()的第二个参数… */
#define RTF_REMOTE 0 /* 远程主机产生的通信 */
#define RTF_LOCAL 1 /* 本地产生的通信 */
#define RT_BPSIZE 100 /* 路由的最大数量 */
/* RTFREE – 删除一个路由引用(假定持有ri_mutex) */
#define RTFREE(prt)
if (–prt->rt_refcnt <= 0) {
freebuf(prt);
}
extern struct rtinfo Route;
extern struct route *rttable[];
int rtadd(IPaddr, IPaddr, IPaddr, unsigned, unsigned, unsigned);
int rtdel(IPaddr, IPaddr), rthash(IPaddr), rtfree(struct route *);
struct route *rtget(IPaddr, Bool);
void rtinit(void);
void ipredirect(struct ep *, unsigned, struct route *);
void ipdbc(unsigned, struct ep *, struct route *);
5 路由的生成源及保持时间
选路表项的易失性与它的来源有关(从备份存储器中得到,ICMP或选路协议,网络管理员手动操作),但为了排除网络中的路由问题,管理员可以推翻任何路由并建立不可改变的永久的路由
6 为数据报选择路由
6.1 实用过程
/* netnum.c - netnum */
#include
#include
#include
/*————————————————————————
* netnum – 计算一个给定IP 地址的网络部分
*————————————————————————
*/
IPaddr
netnum(IPaddr ipa)
{
IPaddr mask = ~0;
if (IP_CLASSA(ipa)) mask = hl2net(0xff000000);
if (IP_CLASSB(ipa)) mask = hl2net(0xffff0000);
if (IP_CLASSC(ipa)) mask = hl2net(0xffffff00);
return ipa & mask; /* 返回一个主机地址字节为全0的地址*/
}
/* netmatch.c – netmatch */
#include
#include
#include
/*————————————————————————
* netmatch – 是否是这个网络上的地址?
*————————————————————————
*/
Bool
netmatch(IPaddr dst, IPaddr net, IPaddr mask, Bool islocal)
{
if ((dst & mask) != (net & mask)) /* 目的地址与选路表中地址比较*/
return FALSE;
/*
* 源地址为本地可以只匹配单播地址 (主机为路由)
*/
if (islocal) /* 如果是本地*/
if (isbrc(dst) || IP_CLASSD(dst)) /* 如果目的地址不是广播地址,或不是D类*/
return mask != ip_maskall; /* 并且掩码不为全1,则返回真,否则为假*/
return TRUE;
}
/* netmask.c – netmask */
#include
#include
#include
IPaddr netnum(IPaddr);
/*————————————————————————
* netmask – 为给定网络设定默认掩码
*————————————————————————
*/
IPaddr
netmask(IPaddr net)
{
IPaddr netpart;
int i;
if (net == 0) /* 目的地址为全0,则使用默认路由,返回全0掩码*/
return net;
/* 网络匹配检查 (子网) */
netpart = netnum(net); /* 提取出网络部分*/
for (i=0; i
#include
#include
/*————————————————————————
* rthash – 计算网络的哈希值
*————————————————————————
*/
int
rthash(IPaddr net)
{
int bc = IP_ALEN; /* # 字节数 */
unsigned int hv = 0; /* 哈希值 */
if (IP_CLASSA(net)) bc = 1;
else if (IP_CLASSB(net)) bc = 2;
else if (IP_CLASSC(net)) bc = 3;
else if (IP_CLASSD(net))
return ((net>>24) & 0xf0) % RT_TSIZE; /* D类前4比特乘16再与散列表长度取余数*/
while (bc–)
hv += ((char *)&net)[bc] & 0xff; /* 每8位相加*/
return hv % RT_TSIZE; /* 返回除以散列长度后的余数*/
}
6.2 获得一个路由
/* rtget.c – rtget */
#include
#include
#include
/*————————————————————————
* rtget – 获得一个给定的IP地址的路由
*————————————————————————
*/
struct route *
rtget(IPaddr dest, Bool local)
{
struct route *prt;
int hv;
if (!Route.ri_valid) /* 如果路由的数据结构没被初始化则应该先初始化*/
rtinit();
wait(Route.ri_mutex); /* 等待信号互斥量*/
hv = rthash(dest); /* 计算哈希值*/
for (prt=rttable[hv]; prt; prt=prt->rt_next) {
if (prt->rt_ttl <= 0)
continue; /* 路由过期 */
if (netmatch(dest, prt->rt_net, prt->rt_mask, local)) /* 如果网络地址匹配*/
if (prt->rt_metric < RTM_INF) /* 并且距离量度小于最大的量度*/
break; /* 则退出for循环*/
}
if (prt == 0) /* 如果没有找到匹配的网络地址*/
prt = Route.ri_default; /* 使用默认路由 */
if (prt != 0 && prt->rt_metric >= RTM_INF) /*如果找到匹配且路离量度大于最大的量度*/
prt = 0; /* prt指向0*/
if (prt) {
prt->rt_refcnt++; /* 引用计数加1*/
prt->rt_usecnt++; /* 统计计数加1*/
}
signal(Route.ri_mutex); /* 释放互斥量*/
return prt;
}
6.3 数据结构初始化
/* rtinit.c – rtinit */
#include
#include
#include
#include
struct rtinfo Route;
struct route *rttable[RT_TSIZE];
/*————————————————————————
* rtinit – 初始化路由表
*————————————————————————
*/
void
rtinit(void)
{
int i;
for (i=0; i
#include
#include
extern Bool dorip; /* TRUE 如果我们正在运行的RIP输出 */
extern int rippid; /* 输出的RIP的pid,如果运行 */
/*————————————————————————
* rttimer – 更新TTLS及删除过期路由
*————————————————————————
*/
void
rttimer(unsigned int delta)
{
struct route *prt, *prev;
Bool ripnotify;
int i;
if (!Route.ri_valid) /* 路由未被初始化则返回*/
return;
wait(Route.ri_mutex); /* 等待互斥量*/
ripnotify = FALSE; /* RIP通知关闭*/
for (i=0; i
prt->rt_ttl -= delta; /* 生存时间减去相应的时间*/
if (prt->rt_ttl <= 0) { /* 如果生存时间小于等于0*/
#ifdef RIP /* 条件编译,当打开RIP时*/
if (dorip && prt->rt_metric < RTM_INF) { /*RIP打开且距离小于最大距离*/
prt->rt_metric = RTM_INF; /* 设置距离为最大距离*/
prt->rt_ttl = RIPZTIME; /* 生存时间为无穷*/
ripnotify = TRUE; /* 打开RIP通知*/
continue;
}
#endif /* RIP */
if (prev) { /*如果prev不为空,删除prt指向的表项*/
prev->rt_next = prt->rt_next;
RTFREE(prt);
prt = prev->rt_next;
} else { /*否则说明prt就是第一个表项*/
rttable[i] = prt->rt_next; /*删除第一个表项*/
RTFREE(prt);
prt = rttable[i];
}
continue;
}
prev = prt; /* 指向下一个*/
prt = prt->rt_next; /* 指向下一个*/
}
}
prt = Route.ri_default; /* 使用默认路由*/
if (prt && (prt->rt_ttl
prt->rt_ttl = RIPZTIME; /* 生存时间为无穷*/
} else
#endif /* RIP */
{
RTFREE(Route.ri_default); /* 释放默认路由 */
Route.ri_default = 0; /* 清除默认路由指针*/
}
}
signal(Route.ri_mutex); /* 释放互斥量*/
#ifdef RIP
if (dorip && ripnotify) /* RIP打开并且RIP通知打开*/
send(rippid, 0); /* 发送任何东西,但超时 */
#endif /* RIP */
return;
}
7.1 增加路由
/* rtadd.c – rtadd */
#include
#include
#include
struct route *rtnew(IPaddr, IPaddr, IPaddr, unsigned,unsigned,unsigned);
void rtinit(void);
int rthash(IPaddr);
/*————————————————————————
* rtadd – 添加一个路由到路由表
*————————————————————————
*/
int
rtadd(IPaddr net, IPaddr mask, IPaddr gw, unsigned metric,
unsigned intf, unsigned ttl)
{
struct route *prt, *srt, *prev;
Bool isdup;
int hv, i;
if (!Route.ri_valid) /* 初始化*/
rtinit();
prt = rtnew(net, mask, gw, metric, intf, ttl); /* 建立新的结点*/
if (prt == (struct route *)SYSERR) /* 分配失败则返回错误*/
return SYSERR;
/* 计算,路由在队列中的键 */
prt->rt_key = 0;
for (i=0; i<32; ++i)
prt->rt_key += (mask >> i) & 1;
wait(Route.ri_mutex); /* 等待互斥量*/
/* 默认路由的特殊情况 */
if (net == RT_DEFAULT) { /* 如果网络地址为任意,全0*/
if (Route.ri_default) /* 默认路由不为空*/
RTFREE(Route.ri_default); /* 释放默认路由*/
Route.ri_default = prt; /* 用新的路由代替*/
signal(Route.ri_mutex); /* 释放互斥量*/
return OK;
}
prev = NULL;
hv = rthash(net); /* 计算哈希值*/
isdup = FALSE; /* 是否有相同地址的路由表项*/
/* 查找是否有相同的路由*/
for (srt=rttable[hv]; srt; srt = srt->rt_next) { /*srt 为空则退出for*/
if (prt->rt_key > srt->rt_key) /* */
break;
if (srt->rt_net == prt->rt_net && /* 网络地址和掩码均相同,找到相同的地址的路由*/
srt->rt_mask == prt->rt_mask) {
isdup = TRUE; /* isdup为真*/
break;
}
prev = srt;
}
if (isdup) { /* isdup为真,说明有相同的路由表项*/
struct route *tmprt;
if (srt->rt_gw == prt->rt_gw) { /* 源路由表与新路由表的下一跳相同 */
/* 更新新由表 */
#ifdef RIP /* RIP打开的情况,上边说过很多回了,下边不再多说*/
if (dorip) {
srt->rt_ttl = ttl;
if (srt->rt_metric != metric) {
if (metric == RTM_INF)
srt->rt_ttl = RIPZTIME;
send(rippid, 0);
}
}
#endif /* RIP */
srt->rt_metric = metric; /* 更新距离量度*/
RTFREE(prt); /* 释放prt*/
signal(Route.ri_mutex); /* 释放互斥量*/
return OK;
}
/* else, someone else has a route there… */
if (srt->rt_metric <= prt->rt_metric) { /* 源路由比新路由具有更小的距离并且下一跳地址不同*/
/* 没有更好的路由线路,放弃新的路由 */
RTFREE(prt);
signal(Route.ri_mutex); /* 释放互斥量*/
return OK;
}
#ifdef RIP
else if (dorip)
send(rippid, 0);
#endif /* RIP */
tmprt = srt; /* 执行到这里说明新路由更优,释放旧的路由*/
srt = srt->rt_next;
RTFREE(tmprt);
}
#ifdef RIP
else if (dorip)
send(rippid, 0);
#endif /* RIP */
prt->rt_next = srt; /* 插入新的路由*/
if (prev) /* 插入到链表的中间*/
prev->rt_next = prt;
else /* 插入到链表的开始*/
rttable[hv] = prt;
signal(Route.ri_mutex);
return OK;
}
建立新的结点,很简单不多说了
/* rtnew.c – rtnew */
#include
#include
#include
/*————————————————————————
* rtnew – 创建一个路由结构
*————————————————————————
*/
struct route *
rtnew(IPaddr net, IPaddr mask, IPaddr gw, unsigned metric,
unsigned ifnum, unsigned ttl)
{
struct route *prt;
prt = (struct route *)getbuf(Route.ri_bpool);
if (prt == (struct route *)SYSERR) {
IpRoutingDiscards++;
return (struct route *)SYSERR;
}
prt->rt_net = net;
prt->rt_mask = mask;
prt->rt_gw = gw;
prt->rt_metric = metric;
prt->rt_ifnum = ifnum;
prt->rt_ttl = ttl;
prt->rt_refcnt = 1; /* our caller */
prt->rt_usecnt = 0;
prt->rt_next = NULL;
return prt;
}
7.2 删除路由
/* rtdel.c – rtdel */
#include
#include
#include
/*————————————————————————
* rtdel – 删除给定网络的路由和掩码
*————————————————————————
*/
int
rtdel(IPaddr net, IPaddr mask)
{
struct route *prt, *prev;
int hv, i;
if (!Route.ri_valid) /* 未被初始化则返回出错*/
return SYSERR;
wait(Route.ri_mutex); /* 等待互斥量*/
if (Route.ri_default && /* 默认路由存在并且net参数与之相同,则删除默认路由*/
net == Route.ri_default->rt_net) {
RTFREE(Route.ri_default);
Route.ri_default = 0;
signal(Route.ri_mutex);
return OK;
}
hv = rthash(net); /* 计算哈希值*/
prev = NULL;
/* 查找匹配的路由*/
for (prt = rttable[hv]; prt; prt = prt->rt_next) {
if (net == prt->rt_net &&
mask == prt->rt_mask)
break;
prev = prt;
}
if (prt == NULL) { /* 没有找到匹配的路由*/
signal(Route.ri_mutex);
return SYSERR;
}
if (prev) /* prev不为空,说明匹配的路由在链表中间,并删除结点*/
prev->rt_next = prt->rt_next;
else /* 路由在链表开头*/
rttable[hv] = prt->rt_next;
RTFREE(prt); /* 释放结点*/
signal(Route.ri_mutex); /* 释放互斥量*/
return OK;
}
释放结点用的,没什么可说的,就是使用互斥量,调用一个宏
/* rtfree.c – rtfree */
#include
#include
#include
/*————————————————————————
* rtfree – remove one reference to a route
*————————————————————————
*/
int
rtfree(struct route *prt)
{
if (!Route.ri_valid)
return SYSERR;
wait(Route.ri_mutex);
RTFREE(prt);
signal(Route.ri_mutex);
return OK;
}
8. IP选项处理
没做什么工做,只是分析了一下IP首部中选面长度八位组的信息
/* ipdoopts.c – ipdoopts */
#include
#include
#include
/*————————————————————————
* ipdoopts – do gateway handling of IP options
*————————————————————————
*/
int
ipdoopts(struct netif *pni, struct ep *pep)
{
return OK; /* not implemented yet */
}
/* ipdstopts.c – ipdstopts */
#include
#include
#include
/*————————————————————————
* ipdstopts – do host handling of IP options
*————————————————————————
*/
int
ipdstopts(struct netif *pni, struct ep *pep)
{
struct ip *pip = (struct ip *)pep->ep_data;
u_char *popt, *popend;
int len;
if (IP_HLEN(pip) == IPMHLEN)
return OK;
popt = pip->ip_data;
popend = (u_char *)&pep->ep_data[IP_HLEN(pip)];
/* NOTE: options not implemented yet */
/* delete the options */
len = pip->ip_len-IP_HLEN(pip); /* data length */
if (len)
memcpy(pip->ip_data, &pep->ep_data[IP_HLEN(pip)], len);
pip->ip_len = IPMHLEN + len;
pip->ip_verlen = (pip->ip_verlen&0xf0) | IP_MINHLEN;
return OK;
}
问题:rtdel调用rtfree而不是使用宏 RTFREE,结果会怎么样? 会发生死锁
IP 总体结构 详解
1.中心环节
IP是整个协议软件的中心环节,不要把IP软件简单的分割成输入和输出两部分,因为输入和输出的界限很模糊.以下把重点放在网关上.
2. IP软件设计思想
* 统一的输入队列以及统一的选路过程
* 独立的IP进程
* 本地主机接口
3. IP软件结构和数据报流程
4. IP软件结构和数据报流程
4.1 选择传入数据报的策略
挑选数据报并为其选择路由的IP程序段实现了一个重要策略:它决定了数据报来源的相对优先级.
公平分配优先权,例用策略为循环法(round-robin)
/* ipgetp.c – ipgetp */
#include <conf.h>
#include <kernel.h>
#include <network.h>
#include <proc.h>
static int ifnext = NI_LOCAL; //接口索引
/*————————————————————————
* ipgetp — choose next IP input queue and extract a packet
*————————————————————————
*/
struct ep *
ipgetp(int *pifnum)
{
struct ep *pep; //以太帧结构体
int i;
recvclr(); /* 确保没有旧分组正在等待 */
while (TRUE) {
for (i=0; i < Net.nif; ++i, ++ifnext) { //遍历每个接口
if (ifnext >= Net.nif) //等于或大于最大接口数
ifnext = 0;
if (nif[ifnext].ni_state == NIS_DOWN) //此接口关闭
continue;
if (pep = NIGET(ifnext)) { /*NIGET宏,提取并返回第一个数据*/
*pifnum = ifnext; //返回接口的序号
return pep; //返回以太帧的结构体指针
}
}
ifnext = receive(); //如没有数据则阻塞,当有数据到达时,返回数据报到达的接口指向
}
/* can't reach here */
}
4.2 IP使用的常量定义
/* ip.h – IP_HLEN, IP_CLASS{A,B,C,D,E} */
/* 互联网协议(IP)的常量和数据报格式 */
#define IP_ALEN 4 /* 以字节为单位的IP地址的长度(字节) */
typedef unsigned long IPaddr; /* 互联网地址 */
#if BYTE_ORDER == BIG_ENDIAN
#define IP_CLASSA(x) (((x) & 0x80000000) == 0) /* A类的IP */
#define IP_CLASSB(x) (((x) & 0xc0000000) == 0x80000000) /* B类的IP */
#define IP_CLASSC(x) (((x) & 0xe0000000) == 0xc0000000) /* C类的IP */
#define IP_CLASSD(x) (((x) & 0xf0000000) == 0xe0000000) /* D类的IP */
#define IP_CLASSE(x) (((x) & 0xf8000000) == 0xf0000000) /* E类的IP */
#else /* BYTE_ORDER */
#define IP_CLASSA(x) (((x) & 0x80) == 0x00) /* A类的IP地址 */
#define IP_CLASSB(x) (((x) & 0xc0) == 0x80) /* B类的IP地址 */
#define IP_CLASSC(x) (((x) & 0xe0) == 0xc0) /* C类的IP地址 */
#define IP_CLASSD(x) (((x) & 0xf0) == 0xe0) /* D类的IP地址 */
#define IP_CLASSE(x) (((x) & 0xf8) == 0xf0) /* E类的IP地址 */
#endif /* BYTE_ORDER */
/* 部分分配协议编号 */
#define IPT_ICMP 1 /* ICMP数据包协议类型 */
#define IPT_IGMP 2 /* IGMP数据包协议类型 */
#define IPT_TCP 6 /* TCP数据包协议类型 */
#define IPT_EGP 8 /* EGP数据包协议类型 */
#define IPT_UDP 17 /* UDP数据包的协议类型 */
#define IPT_OSPF 89 /* OSPF数据包协议类型 */
struct ip {
u_char ip_verlen; /* IP版本及头长度 (in longs)*/
u_char ip_tos; /* 服务类型 */
u_short ip_len; /* 包总长度(字节) */
short ip_id; /* 数据包的id */
short ip_fragoff; /* 碎片偏移(8字节的) */
u_char ip_ttl; /* 生存时间,在网关的跳 */
u_char ip_proto; /* IP协议(见IPT_ *)*/
short ip_cksum; /* 头校验和 */
IPaddr ip_src; /* 源IP地址 */
IPaddr ip_dst; /* 目的地IP地址 */
u_char ip_data[1]; /* 可变长度的数据 */
};
#define IP_VERSION 4 /* 当前版本值 */
#define IP_MINHLEN 5 /* 最小的IP头长度 (in longs) */
#define IP_TTL 255 /* 生存时间初始值 */
#define IP_MF 0x2000 /* 更多的碎片位 */
#define IP_DF 0x4000 /* 不分片位 */
#define IP_FRAGOFF 0x1fff /* 碎片偏移 fragment offset mask*/
#define IP_PREC 0xe0 /* 优先的服务 precedence portion of TOS*/
/* IP优先值 */
#define IPP_NETCTL 0xe0 /* 网络控制 */
#define IPP_INCTL 0xc0 /* Internet控制 */
#define IPP_CRIT 0xa0 /* 关键 critical */
#define IPP_FLASHO 0x80 /* flash over-ride */
#define IPP_FLASH 0x60 /* flash */
#define IPP_IMMED 0x40 /* immediate */
#define IPP_PRIO 0x20 /* 优先 */
#define IPP_NORMAL 0x00 /* 正常 */
/*宏来计算一个数据报的报头的长度(字节) */
#define IP_HLEN(pip) ((pip->ip_verlen & 0xf)<<2)
#define IPMHLEN 20 /* 最小的IP头长度(字节) */
/* IP选项 */
#define IPO_COPY 0x80 /* 分片复制 copy on fragment mask */
#define IPO_CLASS 0x60 /* 选项类 option class */
#define IPO_NUM 0x17 /* 选项编号option number */
#define IPO_EOOP 0x00 /* 选项结束 */
#define IPO_NOP 0x01 /* 没有操作 no operation */
#define IPO_SEC 0x82 /* DoD security/compartmentalization */
#define IPO_LSRCRT 0x83 /* 松散源路由 loose source routing */
#define IPO_SSRCRT 0x89 /* 严格的源路由strict source routing */
#define IPO_RECRT 0x07 /* 记录路线 */
#define IPO_STRID 0x88 /* 流编号 */
#define IPO_TIME 0x44 /* 互联网时间戳 */
#define IP_MAXLEN BPMAXB-EP_HLEN /* IP数据报的最大长度 */
/*IP进程的信息 */
extern PROCESS ipproc();
#define IPSTK 512 /* IP过程堆栈大小 */
#define IPPRI 100 /* IP运行在高优先级 */
#define IPNAM "ip" /* IP过程的名字 */
#define IPARGC 0 /* count of args to IP */
extern IPaddr ip_maskall; /* = 255.255.255.255 */
extern IPaddr ip_anyaddr; /* = 0.0.0.0 */
extern IPaddr ip_loopback; /* = 127.0.0.1 */
extern int ippid, gateway;
struct ip *iph2net(struct ip *), *ipnet2h(struct ip *);
unsigned short cksum(WORD *, unsigned);
int ipsend(IPaddr, struct ep *, unsigned, u_char, u_char, u_char);
int ipputp(unsigned, IPaddr, struct ep *);
Bool isbrc(IPaddr);
4.3 IP进程的结构 (IP进程允许被阻塞)
/* ipproc.c – ipproc */
#include <conf.h>
#include <kernel.h>
#include <network.h>
struct ep *ipgetp(int *);
struct route *rtget(IPaddr, Bool);
/*————————————————————————
* ipproc – 处理一个从网络中来的IP数据包
*————————————————————————
*/
PROCESS
ipproc(void)
{
struct ep *pep;
struct ip *pip;
struct route *prt;
Bool nonlocal;
int ifnum;
ippid = getpid(); /* 得到进程的ID */
signal(Net.sema); /* 信号进行初始化*/
while (TRUE) {
pep = ipgetp(&ifnum); /* 选取一个以太网数据报*/
pip = (struct ip *)pep->ep_data; /* 得到此报包含的更高级报地址*/
if ((pip->ip_verlen>>4) != IP_VERSION) { /* 判断是否为IP数据报*/
IpInHdrErrors++;
freebuf(pep);
continue;
}
if (IP_CLASSE(pip->ip_dst)) { /* 判断是否为E类地址*/
IpInAddrErrors++;
freebuf(pep);
continue;
}
if (ifnum != NI_LOCAL) { /* 此报不是本机产生的*/
if (cksum((WORD *)pip, IP_HLEN(pip))) { /* 计算检验和*/
IpInHdrErrors++;
freebuf(pep);
continue;
}
ipnet2h(pip);
pep->ep_order |= EPO_IP;
}
prt = rtget(pip->ip_dst, (ifnum == NI_LOCAL)); /* 选择路由*/
if (prt == NULL) { /* 如果路由不存在*/
if (gateway) { /* 如网关存在发送ICMP不可达*/
iph2net(pip);
pep->ep_order &= ~EPO_IP;
icmp(ICT_DESTUR, ICC_NETUR,
pip->ip_src, pep, 0);
} else {
IpOutNoRoutes++;
freebuf(pep);
}
continue;
}
nonlocal = ifnum != NI_LOCAL && prt->rt_ifnum != NI_LOCAL; /* 不是本地地址*/
if (!gateway && nonlocal) { /* 不是网关也不是本地地址*/
IpInAddrErrors++;
freebuf(pep);
rtfree(prt);
continue;
}
if (nonlocal)
IpForwDatagrams++;
/* 如果我们发件人,填写在源IP */
if (ifnum == NI_LOCAL) { /* 如果网络接口为本地*/
if (pip->ip_src == ip_anyaddr)
if (prt->rt_ifnum == NI_LOCAL) /* 路由的接口为本地*/
pip->ip_src = pip->ip_dst;
else
pip->ip_src =
nif[prt->rt_ifnum].ni_ip;
} else if (–(pip->ip_ttl) == 0 && /* ttl 为零,且路由接口不为本地*/
prt->rt_ifnum != NI_LOCAL) {
IpInHdrErrors++;
iph2net(pip);
pep->ep_order &= ~EPO_IP;
icmp(ICT_TIMEX, ICC_TIMEX, pip->ip_src, pep, 0); /*发送ICMP超时报文*/
rtfree(prt);
continue;
}
ipdbc(ifnum, pep, prt); /* 处理定向广播 */
ipredirect(pep, ifnum, prt); /* 做重定向,如果需要的话*/
if (prt->rt_metric != 0)
ipputp(prt->rt_ifnum, prt->rt_gw, pep);
else
ipputp(prt->rt_ifnum, pip->ip_dst, pep);
rtfree(prt);
}
}
int ippid, gateway, bsdbrc;
4.4 校验和的计算
/* cksum.c – cksum */
/*————————————————————————
* cksum – Return 16-bit ones complement of 16-bit ones complement sum
*————————————————————————
*/
unsigned short
cksum(buf, nbytes)
unsigned short *buf;
int nbytes;
{
unsigned long sum;
unsigned short tmp;
int nwords;
nwords = nbytes / 2; /* 将字节转成字,也就是16个的个数 */
for (sum=0; nwords>0; nwords–) /* 将16位为单位做累加*/
sum += *buf++;
if (nbytes & 1) { /* 如长度不是16位的倍数则补齐*/
tmp = *(unsigned char *)buf;
sum += tmp;
}
sum = (sum >> 16) + (sum & 0xffff); /* 高位低位相加 */
sum += (sum >> 16); /* 上一步溢出时,将溢出位也加到sum中 */
return (unsigned short)~sum; /* 返回sum的反码*/
}
4.5 处理定向广播
主要做了两件事,复制一个副本,然后正常发送
/* ipdbc.c – ipdbc */
#include <conf.h>
#include <kernel.h>
#include <network.h>
struct route *rtget(IPaddr, Bool);
/*————————————————————————
* ipdbc – handle IP directed broadcast copying
*————————————————————————
*/
void
ipdbc(unsigned ifnum, struct ep *pep, struct route *prt)
{
struct ip *pip = (struct ip *)pep->ep_data;
struct ep *pep2;
struct route *prt2;
int len;
if (prt->rt_ifnum != NI_LOCAL)
return; /* 不是我们 */
if (!isbrc(pip->ip_dst))
return; /* 不是广播 */
prt2 = rtget(pip->ip_dst, RTF_LOCAL); /* 选择一个路由 */
if (prt2 == NULL)
return;
if (prt2->rt_ifnum == ifnum) { /* 没有针对接口 */
rtfree(prt2);
return;
}
/* 定向广播,建立一个副本 */
/* len = ether header + IP packet */
len = EP_HLEN + pip->ip_len;
if (len > EP_MAXLEN) /* 为副本分配缓冲区*/
pep2 = (struct ep *)getbuf(Net.lrgpool);
else
pep2 = (struct ep *)getbuf(Net.netpool);
if (pep2 == (struct ep *)SYSERR) {
rtfree(prt2);
return;
}
memcpy(pep2, pep, len); /* 复制副本*/
/* 发送一份拷贝到网络 */
ipputp(prt2->rt_ifnum, pip->ip_dst, pep2);
rtfree(prt2);
return; /* continue; "pep" goes locally in IP */
}
4.6 识别一个广播地址
/* isbrc.c – isbrc */
#include <conf.h>
#include <kernel.h>
#include <sleep.h>
#include <network.h>
/*————————————————————————
* isbrc – Is "dest" a broadcast address?
*————————————————————————
*/
Bool
isbrc(IPaddr dest)
{
int inum;
/* 所有的0和全1的是广播地址 */
if (dest == ip_anyaddr || dest == ip_maskall) /* 如果为全0 或 全1 则返回真*/
return TRUE;
/* 检查真正的广播地址和BSD风格的网和子网 */
for (inum=0; inum < Net.nif; ++inum)
if (dest == nif[inum].ni_brc ||
dest == nif[inum].ni_nbrc ||
dest == nif[inum].ni_subnet ||
dest == nif[inum].ni_net)
return TRUE;
return FALSE;
}
5. IP首部中的字节顺序
/* iph2net.c – iph2net */
#include <conf.h>
#include <kernel.h>
#include <network.h>
/*————————————————————————
* iph2net – iph2net – 转换成一个IP数据包头从主机到网络字节顺序
*————————————————————————
*/
struct ip *
iph2net(struct ip *pip)
{
/* 注:不包括IP选项 */
pip->ip_len = hs2net(pip->ip_len);
pip->ip_id = hs2net(pip->ip_id);
pip->ip_fragoff = hs2net(pip->ip_fragoff);
return pip;
}
/* ipnet2h.c – ipnet2h */
#include <conf.h>
#include <kernel.h>
#include <network.h>
/*————————————————————————
* ipnet2h – 转换成一个IP数据包头从网络到主机字节顺序
*————————————————————————
*/
struct ip *
ipnet2h(struct ip *pip)
{
/* 注:不包括IP选项 */
pip->ip_len = net2hs(pip->ip_len);
pip->ip_id = net2hs(pip->ip_id);
pip->ip_fragoff = net2hs(pip->ip_fragoff);
return pip;
}
6. 向IP发送数据报
6.1 发送本地生成的数据报
/* ipsend.c – ipsend */
#include <conf.h>
#include <kernel.h>
#include <network.h>
#include <proc.h>
static ipackid = 1; /* 静态变量 标识*/
/*————————————————————————
* ipsend – 发送一个IP数据报到指定地址
*————————————————————————
*/
int
ipsend(IPaddr faddr, struct ep *pep, unsigned datalen,
u_char proto, u_char ptos, u_char ttl)
{
struct ip *pip = (struct ip *) pep->ep_data;
pep->ep_type = EPT_IP; /* 类型为网际协议*/
pep->ep_order |= EPO_IP|EPO_NET; /* 网络层 协议等级为1*/
pip->ip_verlen = (IP_VERSION<<4) | IP_MINHLEN; /* 协议版本 最小的IP头长度*/
pip->ip_tos = ptos; /* 设置服务类型与优先级*/
pip->ip_len = datalen+IP_HLEN(pip); /* IP分组的长度*/
pip->ip_id = ipackid++; /* 分组的标识*/
pip->ip_fragoff = 0; /* 分片的偏移*/
pip->ip_ttl = ttl; /* 生存时间*/
pip->ip_proto = proto; /* 协议类型*/
pip->ip_dst = faddr; /* 目标地址*/
/*
* 特殊情况的ICMP协议,因此源匹配目的地
* on multi-homed hosts. 多穴主机??
*/
if (pip->ip_proto != IPT_ICMP) /* 不是ICMP分组*/
pip->ip_src = ip_anyaddr; /* IP的源地址为任意地址*/
if (enq(nif[NI_LOCAL].ni_ipinq, pep, 0) < 0) { /* 将分组放入本地主机接口队列中*/
freebuf(pep);
IpOutDiscards++;
}
send(ippid, NI_LOCAL); /* IP数据报阻塞并等待,发送报文给IP进程*/
IpOutRequests++;
return OK;
}
/* 特殊的IP地址 */
IPaddr ip_anyaddr = 0;
#if BYTE_ORDER == LITTLE_ENDIAN
IPaddr ip_loopback = 0x0100007F; /* 127.0.0.1 */
#else /* BYTE_ORDER */
IPaddr ip_loopback = 0x7F000001; /* 127.0.0.1 */
#endif /* BYTE_ORDER */
6.2 发送传入数据报
/* ip_in.c – ip_in */
#include <conf.h>
#include <kernel.h>
#include <network.h>
#include <proc.h>
/*————————————————————————
* ip_in – IP input function
*————————————————————————
*/
int
ip_in(struct netif *pni, struct ep *pep)
{
struct ip *pip = (struct ip *)pep->ep_data;
IpInReceives++;
if (enq(pni->ni_ipinq, pep, pip->ip_tos & IP_PREC) < 0) {
IpInDiscards++; /* 如队列满则记录溢出差错并丢则报文*/
freebuf(pep);
}
send(ippid, (pni-&nif[0])); /* 向IP进程发送消息*/
return OK;
}
7. 表格的维护
/* slowtimer.c – slowtimer */
#include <conf.h>
#include <kernel.h>
#include <proc.h>
#include <sleep.h>
#include <date.h>
#include <network.h>
#define STGRAN 1 /* 定时器粒度(延迟秒) */
void arptimer(unsigned), ipftimer(unsigned), rttimer(unsigned);
#ifdef OSPF
void ospftimer(unsigned);
#endif /*OSPF*/
/*————————————————————————
* slowtimer – 处理长期定期维护网络表
*————————————————————————
*/
PROCESS
slowtimer(void)
{
unsigned long lasttime, now; /* prev and current times (secs)*/
int delay; /* 几秒钟内实际延迟 */
signal(Net.sema);
gettime(&lasttime);
while (1) {
sleep(STGRAN); /* 延时*/
gettime(&now);
delay = now – lasttime;
if (delay <= 0 || delay > 4*STGRAN)
delay = STGRAN; /* 时钟复位-likely clock reset */
lasttime = now;
arptimer(delay);
ipftimer(delay);
rttimer(delay);
#ifdef OSPF
ospftimer(delay);
#endif /* OSPF */
}
}
linux 使用 vi 编辑 16进制
用法很简单:
在vi的命令状态下
:%!xxd ——将当前文本转换为16进制格式。
:%!od ——将当前文本转换为16进制格式。
:%!xxd -c 12——将当前文本转换为16进制格式,并每行显示12个字节。
:%!xxd -r ——将当前文件转换回文本格式。
linux mplayer 字幕乱码 解决
1. 在~/.mplayer/config里加一行subcp=cp936(通常是这个编码)就行了,虽然指定了,但为什么字幕 变成下划线了呢,因为没有指定字体
2. 直接指定系统字体的名字,列如,在~/.mplayer/config加上这样一行 font='simhei'就可以了,这样一来,指定一个漂亮的字体就行了,例如simhei,只要把这个字体 文件拷贝到/usr/share/fonts/zh_CN/TrueType/,再运行一下fc-cache,然后指定font='SimHei'
3.运行mplayer 配置菜单里的subtitles & OSD 下面的encoding 选cp936
font里的font 指定字体文件就可以了