一年了,IP被封了,我一直没弄,今天查了查资料,发现换IP也没那么麻烦,一下午时间,换好了,以后又可以写博客了
dlink 714p+ 打印机驱动
找了好久才找到的
微星 785GTM-E45 自制串口线
购入jlink 自制 转接线
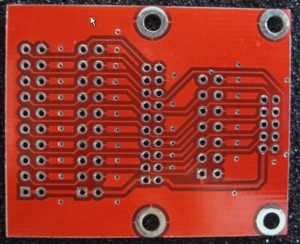
晕菜到家了,买了jlink没买转换板,发的6410的版是2.0间距的10p的口,在淘宝上买板,这不是放假人家不发货,而且还没线卖,我要板没线还是用不了。一气之下,自己做了一条转换线。10p FC头,是以前买来做jtag线用的,20p fc头没有,用的dma33的ide线的头,拆了,锯开,打磨,用502粘上的,10p 2.54转2.0是用从老的磨托罗拉的BP机的板子上拆下来的单排母口做的,哈哈。接口定义如下,上图.留给有用的朋友
s3c_6410(亚嵌发的那个)
1 VDD_IO 电源 3.3V(输入)
2 VDD_IO 电源 3.3V(输入)
3 TRSTn TRSTn
4 nRESET nRESET
5 TDI TDI
6 TDO TDO
7 TMS TMS
8 GND 地
9 TCK TCK
10 GND 地
jlink v8 (20PIN)
1 vref
2 vcc(VTARGET)
3 TRST_N
5 TDI
7 TMS
9 TCK
11 RTCK
13 TDO
15 SRST_N
17 DBGRQ(Wiggler)
19 DBGACK(Wiggler)
other: GND
转换关系
jlink 20 -> 10pin
1 1 (1,2连在一起)
2 2 (1,2连在一起)
3 3
5 5
7 7
8 8
9 9
10 10
15 4
13 6
由于开发板的p1,p2本来就是连在一起的,所以1->1,2->2就行了
SEGGER J-Link Commander V4.26b ('?' for help)
Compiled May 20 2011 17:18:29
DLL version V4.26b, compiled May 20 2011 17:18:15
Firmware: J-Link ARM V8 compiled Apr 27 2011 20:42:35
Hardware: V8.00
S/N: 20100214
Feature(s): RDI,FlashDL,FlashBP,JFlash,GDBFull
VTarget = 3.248V
Info: TotalIRLen = 9, IRPrint = 0x0011
Found 2 JTAG devices, Total IRLen = 5:
#0 Id: 0x2B900F0F, IRLen: 04, IRPrint: 0x0, ARM ETB
#1 Id: 0x07B76F0F, IRLen: 05, IRPrint: 0x1, ARM1176 Core
ARM11 identified.
JTAG speed: 100 kHz
J-Link>
ARP 功击与抓包代码
上课的地方arp横行,总是上不去网。
研究了一下arp功击的代码。总用更高的频率来解决功击网关的问题,失败告终。
抓包
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <linux/if_packet.h>
#include <linux/if_ether.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <net/if.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
void print_arp(unsigned char *a,int len)
{
int i;
char ccc='1';
for(i=0;i<len;i++){
if(i==6 || i==12 || i==14 || i==16 || i==18 || i==19 || i==20 || i==22 || i==28 || i==32 || i==38 || i==42)
putchar('|');
if((i>=28 && i<=31) || (i>=38 && i<=41))
printf("%d.",a[i]);
else
printf("%02x",a[i]);
//fflush(stdout);
}
putchar('n');
}
void print_eth(unsigned char *a,int len)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<len;i++){
printf("%02x",a[i]);
}
putchar('n');
}
int set_promisc(char *interface, int fd) {
struct ifreq ifr;
strcpy(ifr.ifr_name, interface);
if(ioctl(fd, SIOCGIFFLAGS, &ifr) == -1) {
perror("iotcl()");
return -1;
}
ifr.ifr_flags |= IFF_PROMISC;
if(ioctl(fd, SIOCSIFFLAGS, &ifr) == -1) {
perror("iotcl()");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int sock, n;
unsigned char buffer[2048];
unsigned char *iphead, *ethhead;
struct sockaddr_ll sll;
// if(argc != 3){
// printf("need interface name and protocol as argumentsn");
// return -1;
// }
if ( (sock=socket(PF_PACKET, SOCK_RAW,
htons(ETH_P_ARP)))<0) {
perror("socket");
exit(1);
}
sll.sll_family = PF_PACKET;
// sll.sll_ifindex = Get_IfaceIndex(sock,argv[1]); //通过此处传入网络设备接口
struct ifreq ifstruct;
strcpy(ifstruct.ifr_name, "eth0");
//sll.sll_protocol = htons(atoi(argv[2]));
sll.sll_protocol=htons(ETH_P_ARP);
if(bind(sock,(struct sockaddr *)(&sll),sizeof(sll))==-1)
{
printf("bind error:%s !n",strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
//int set_promisc(char *interface, int fd) {
if(set_promisc("eth0",sock) == -1)
{
printf("BLUE set promisc failed !n");
return -1;
}
while (1) {
printf("—–recive start—–n");
n = recvfrom(sock,buffer,2048,0,NULL,NULL);
printf("%d bytes readn",n);
printf("index:%dn",sll.sll_ifindex );
/* Check to see if the packet contains at least
* complete Ethernet (14), IP (20) and TCP/UDP
* (8) headers.
*/
if (n<42) {
perror("recvfrom():");
printf("Incomplete packet (errno is %d)n",
errno);
close(sock);
exit(0);
}
ethhead = buffer;
printf("Destination MAC address: "
"%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02xn",
ethhead[0],ethhead[1],ethhead[2],
ethhead[3],ethhead[4],ethhead[5]);
printf("Source MAC address: "
"%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02xn",
ethhead[6],ethhead[7],ethhead[8],
ethhead[9],ethhead[10],ethhead[11]);
printf("protocal:"
"0x%02x%02xn",ethhead[12],ethhead[13]);
iphead = buffer+14; /* Skip Ethernet header */
if (*iphead==0x45) { /* Double check for IPv4
* and no options present */
printf("Source host %d.%d.%d.%dn",
iphead[12],iphead[13],
iphead[14],iphead[15]);
printf("Dest host %d.%d.%d.%dn",
iphead[16],iphead[17],
iphead[18],iphead[19]);
printf("Source,Dest ports %d,%dn",
(iphead[20]<<8)+iphead[21],
(iphead[22]<<8)+iphead[23]);
printf("Layer-4 protocol %dn",iphead[9]);
}
//print_eth(1,buffer,512);
print_arp(ethhead,48);
// print_eth(ethhead,n);
}
}
功击
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <linux/if_packet.h>
#include <linux/if_ether.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <net/if.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
void print_eth(unsigned char *a,int len)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<len;i++){
printf("%02x",a[i]);
}
putchar('n');
}
int set_promisc(char *interface, int fd) {
struct ifreq ifr;
strcpy(ifr.ifr_name, interface);
if(ioctl(fd, SIOCGIFFLAGS, &ifr) == -1) {
perror("iotcl()");
return -1;
}
ifr.ifr_flags |= IFF_PROMISC;
if(ioctl(fd, SIOCSIFFLAGS, &ifr) == -1) {
perror("iotcl()");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv){
int sock;
char SendBuffer[64];
char intfname[16];
struct sockaddr_ll dest;
struct sockaddr_ll sll;
memset(&dest,0,sizeof(dest));
memset(&sll,0,sizeof(sll));
strcpy(intfname,argv[1]);
dest.sll_family=AF_PACKET;
dest.sll_protocol=htons(ETH_P_ALL);
if ( (sock=socket(PF_PACKET, SOCK_RAW,
htons(ETH_P_ALL)))<0) {
perror("socket");
exit(1);
}
sll.sll_family = AF_PACKET;
// sll.sll_ifindex = Get_IfaceIndex(sock,intfname);
struct ifreq ifstruct;
strcpy(ifstruct.ifr_name, "eth0");
sll.sll_protocol = htons(ETH_P_ALL);
dest.sll_ifindex =sll.sll_ifindex;
dest.sll_halen = 6;
memcpy((char*)dest.sll_addr,SendBuffer,6);
if(bind(sock,(struct sockaddr *)(&sll),sizeof(sll))==-1)
{
printf("bind error!!n");
return 0;
}
if(set_promisc("eth0",sock) == -1)
{
printf("BLUE set promisc failed !n");
return 0;
}
printf("nnnn—-send start——n");
print_eth(SendBuffer,64);
sendto(sock,&SendBuffer,64,0,(struct sockaddr *)(&dest),sizeof(dest));
//printf("send to %x:%x:%x:%x:%x:%xn",dest.sll_addr[0],dest.sll_addr[1],dest.sll_addr[2],dest.sll_addr[3],dest.sll_addr[4],dest.sll_addr[5]);
printf("—send success—-n");
return 0;
}
原文件下载:
maze – 回溯法解决迷宫
#include <stdio.h>
struct point {
int row;
int col;
};
/* define point stack */
struct point stack[512];
/* define stack pointer */
int top = 0;
/* define push() */
void push(struct point node)
{
stack[top++] = node;
return;
}
/* define pop() */
struct point pop(void)
{
return stack[–top];
}
/* define isempty() */
int isempty(void)
{
return (top == 0);
}
int maze[5][5] =
{
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 1, 0 }
};
struct point father[5][5] =
{
{{-1,-1}, {-1,-1}, {-1,-1}, {-1,-1}, {-1,-1} },
{{-1,-1}, {-1,-1}, {-1,-1}, {-1,-1}, {-1,-1} },
{{-1,-1}, {-1,-1}, {-1,-1}, {-1,-1}, {-1,-1} },
{{-1,-1}, {-1,-1}, {-1,-1}, {-1,-1}, {-1,-1} },
{{-1,-1}, {-1,-1}, {-1,-1}, {-1,-1}, {-1,-1} },
};
void print_stack(void)
{
int i;
for (i = top-1; i >= 0; i–)
printf("(%d, %d) n", stack[i].row, stack[i].col);
printf("————————n");
return;
}
void print_maze(void)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
printf("%d ", maze[i][j]);
}
printf("n");
}
printf("————————n");
return;
}
void print_father(void)
{
int i, j;
struct point node;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
node = father[i][j];
printf("(%2d,%2d) ", node.row, node.col);
}
printf("n");
}
printf("————————n");
return;
}
struct point entry = {0, 0};
struct point out = {4, 4};
void backtrack(struct point p)
{
/* define tmp node = curr point */
struct point node = p;
struct point null = {-1, -1};
struct point top, topfather;
int row, col;
#ifdef DEBUG
printf("backtrack is begin n");
print_stack();
getchar();
#endif
/* peak stack top */
top = pop();
push(top);
/* get top father */
topfather = father[top.row][top.col];
while(1)
{
/* get curr node's row & col */
row = node.row;
col = node.col;
/* clear maze[][] = 0 */
maze[row][col] = 0;
/* get current node's father */
node = father[row][col];
/* clear father[][] = (-1,-1) */
father[row][col] = null;
#ifdef DEBUG
print_maze();
print_father();
getchar();
#endif
/* end condition */
/* peak stack top point -> topfather */
/* if node == topfather, break */
if (node.row == topfather.row && node.col == topfather.col)
break;
}
// printf("backtrack is over n");
}
void print_solution(void)
{
/* define tmp node = exit point */
struct point node = out;
int row, col;
static int counter = 0;
while(1)
{
/* print curr node */
printf("(%d, %d) <- ", node.row, node.col);
row = node.row;
col = node.col;
/* get current node's father */
node = father[row][col];
/* if current node is (-1,-1), then break */
if (node.row == -1)
break;
}
printf("n");
printf("%d solution is over n", ++counter);
return;
}
int main(void)
{
//struct point entry = {2, 2};
struct point curr;
struct point node;
int flag = 0;
printf("hello, mazer!n");
/* init stack, push entry point */
push(entry);
#ifdef DEBUG
print_stack();
print_maze();
print_father();
#endif
while (!isempty())
{
/* get the stack top */
curr = pop();
/* flag curr point */
maze[curr.row][curr.col] = 2;
/* check it */
// print_stack();
// print_maze();
/* judgement if curr is exit point */
if (curr.row == out.row && curr.col == out.col)
{
printf("one solution found! n");
print_solution();
/* begin to backtrack */
backtrack(curr);
// break;
continue;
}
/* expand from curr */
flag = 0;
/* look left */
if (curr.col-1 >= 0 && maze[curr.row][curr.col-1] == 0)
{
/* push left point */
node.row = curr.row;
node.col = curr.col – 1;
/* node 's father is null */
if (father[node.row][node.col].row == -1)
{
push(node);
/* remember father */
father[node.row][node.col] = curr;
flag++;
}
}
/* look up */
if (curr.row-1 >= 0 && maze[curr.row-1][curr.col] == 0)
{
/* push up point */
node.row = curr.row – 1;
node.col = curr.col;
if (father[node.row][node.col].row == -1)
{
push(node);
/* remember father */
father[node.row][node.col] = curr;
flag++;
}
}
/* look right */
if (curr.col+1 < 5 && maze[curr.row][curr.col+1] == 0)
{
/* push right point */
node.row = curr.row;
node.col = curr.col + 1;
if (father[node.row][node.col].row == -1)
{
push(node);
/* remember father */
father[node.row][node.col] = curr;
flag++;
}
}
/* look down */
if (curr.row+1 < 5 && maze[curr.row+1][curr.col] == 0)
{
/* push down point */
node.row = curr.row + 1;
node.col = curr.col;
if (father[node.row][node.col].row == -1)
{
push(node);
/* remember father */
father[node.row][node.col] = curr;
flag++;
}
}
#ifdef DEBUG
print_stack();
print_father();
getchar();
#endif
/* if no way out (curr node has no expand node) */
if (flag == 0)
backtrack(curr);
}
printf("maze is over n");
// print_stack();
return 0;
}
bubble – 冒泡排序
#include <stdio.h>
int bubble(int *a,int len)
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<len-1;i++){
for(j=0;j<len-i-1;j++){
if(a[j]>a[j+1]){
a[j]^=a[j+1];
a[j+1]^=a[j];
a[j]^=a[j+1];
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int main(void)
{
int a[]={6,5,4,3,2,1},i;
bubble(a,6);
for(i=0;i<6;i++){
printf("%d ",a[i]);
}
printf("n");
return 0;
}
mergesort – 归并排序
#include <stdio.h>
#define LEN 8
int a[LEN]={5,2,4,7,1,3,2,6};
void merge(int start,int mid,int end)
{
int n1=mid-start+1;
int n2=end-mid;
int left[n1],right[n2];
int i,j,k;
for(i=0;i<n1;i++)
left[i]=a[start+i];
for(j=0;j<n2;j++)
right[j]=a[mid+j+1];
i=j=0;
for(k=start;i < n1 && j <n2;k++){
if(left[i]<right[j]){
a[k]=left[i];
i++;
}
else{
a[k]=right[j];
j++;
}
}
if(i<n1){
for(;i<n1;i++){
a[k]=left[i];
k++;
}
}
if(j<n2){
for(;j<n2;j++){
a[k]=right[j];
k++;
}
}
}
void sort(int start,int end)
{
int mid;
if(start<end){
mid=(start+end)/2;
sort(start,mid);
sort(mid+1,end);
merge(start,mid,end);
}
}
int main(void)
{
int i;
sort(0,LEN-1);
for(i=0;i<LEN;i++){
printf("%d ",a[i]);
}
printf("n");
return 0;
}
insertion – 插入排序
void insertion_sort(int *a,int len)
{
int i,j,key;
for(i=1;i<len;i++){
key=a[i];
j=i-1;
while(j>=0 && a[j]>key){
a[j+1]=a[j];
j–;
}
a[j+1]=key;
}
}
int main(void)
{
int a[]={12,5,9,3,4,7,4,6,2},i;
for(i=0;i<9;i++)
printf("%d ",a[i]);
printf("n");
insertion_sort(a,9);
for(i=0;i<9;i++)
printf("%d ",a[i]);
printf("n");
return 0;
}
halfind – 折半查找
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define LEN 8
int halfind(int *a,int key)
{
int start =0,end=LEN-1,mid;
while(start <= end){
mid=(start+end)/2;
if(a[mid] > key){
end=mid -1;
}
else if(a[mid] < key){
start=mid+1;
}
else
return mid;
}
return -1;
}
int main(int argc,char **argv)
{
int a[]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};
printf("%dn",halfind(a,atoi(argv[1])));
return 0;
}
==============递归方式===============
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define LEN 8
int a[]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};
int halfind(int start,int end,int key)
{
int mid;
if(start <= end){
mid=(start+end)/2;
if(a[mid] > key){
halfind(start,mid -1,key);
}
else if(a[mid] < key){
halfind(mid+1,end,key);
}
else{
printf("%dn",mid);
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main(int argc,char **argv)
{
printf("%dn",halfind(0,LEN-1,atoi(argv[1])));
return 0;
}